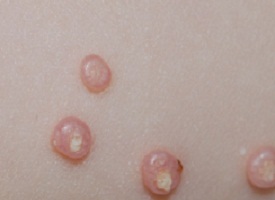
Q-1. A young lady has asymptomatic, dome shaped and small pearly white nodules on forehead for last 2 months. Two year daughter also has similar lesion. Causative agent is
a) HHV 6
b) Coxsackie
c) Pox virus
d) Papilloma virus
Answer: Pox virus
Explanation:
Molluscum contagiosum is an infection caused by a poxvirus.
Lesions may be located anywhere; however, a predilection for the face, trunk, and extremities is observed in children and a predilection for the groin and genitalia is observed in adults.
The lesions are smooth, dome shaped, pearly white papules with central umbilication. Central core can be extruded.
Q-2. Nodulo-cystic acne in a young boy with oily skin. Treatment is
a) Oral isotretinoin
b) Topical retinoic acid
c) Oral steroids
d) Topical antibiotic
Answer: Oral isotretinoin
Explanation:
Treatment of acne:
Mild acne:
Topical retinoid or Benzoyl peroxide
Moderate acne: Predominantly comadonic
Topical retinoid plus Benzoyl peroxide
Moderate acne: Predominantly inflammatory
Oral antibiotics plus retinoid or
Oral antibiotics plus Benzoyl peroxide
Severe acne:
Oral retinoid or anti-androgenic (In female) plus
Topical retinoid or Benzoyl peroxide
Important points:
Nodulo-cystic acne is a severe form of acne affecting the face, chest and back.
The recommended treatment for nodulo-cystic acne is oral isotretinoin, which should be commenced early to prevent scarring.
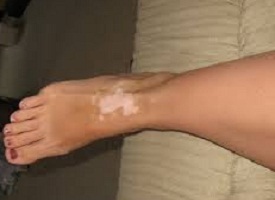
Q-3. 18 year female has hypo-pigmented patch over both ankles. What is not used for treatment?
a) Topical clobetasol
b) Topical tretinoin
c) Topical tacrolimus
d) Topical methoxsalen
Answer: Topical tretinoin
Explanation:
Treatment of vitiligo:
Photo-chemotherapy: PUVA (Psoralen with UV-A)
Phototherapy: UV-B
Corticosteroids
Levamisole
Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus
De-pigmenting agents: Mono-benzyl ether of hydroquinone
Important point:
Topical methoxsalen is Psoralen.
Q-4. Athletic male with itchy lesion at groin, causative agent is A/E
a) Trichophyton
b) Microsporum
c) Epidermophyton
d) Aspergillus
Answer: Aspergillus
Explanation:
Location of dermatophytes: Skin
Trichophyton
Microsporum
Epidermophyton
Location of dermatophytes: Hair
Trichophyton
Microsporum
Location of dermatophytes: Nails
Trichophyton
Epidermophyton
Important point:
Dermatophytes are keratinophilic fungi, living only on superficial dead keratin.
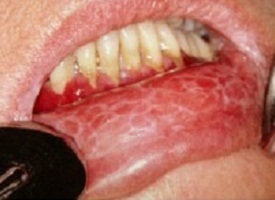
Q-5. Lady with bilateral buccal reticulate white streaks. Pain increase on spicy food intake and pt give no h/o tobacco but shows amalgam on 3rd molar. Diagnosis is
a) Lichen planus
b) Leukoplakia
c) Aphthous stomatitis
d) Candida
Answer: Lichen planus
Explanation:
Clinical features of oral lichen planus:
Reticular lichen planus:
Symmetrical white lace-like pattern on buccal mucosa
May affect tongue or gums and may ulcerate.
Atrophic/erosive lichen planus:
Red lesions often with a whitish border
My cause erosions
Most often affects the gums (gingiva) and lips
Can be very painful
Plaque type:
Usually seen in smokers
Important point:
Lichen planus is a T cell-mediated autoimmune disease, in which inflammatory cells attack an unknown protein within skin and mucosal keratinocytes.
Lesions are most frequently seen on the extremities. It may be associated with mucosal (Oral and genital) lesions and nail and scalp involvement.
Mucosal lesions may asymptomatic or patient may complain of burning sensation especially on the eating spicy food.
Q-6. Oral candidiasis presents with white patch in all except?
a) Acute pseudo-membranous candidiasis
b) Chronic atrophic candidiasis
c) Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
d) Chronic muco-cutaneous candidiasis
Answer: Chronic atrophic candidiasis
Explanation:
Chronic atrophic candidiasis: Also called denture mouth
In denture wearers
Sharply defined areas of erythema and edema on the palate, area in contact with dentures
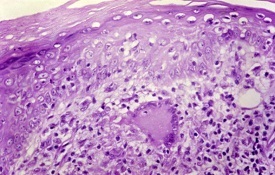
Q-7. Young lady presented with a hypo-anesthetic patch on left forearm. On examination a thickened nerve was palpable. Histopathology as shown in following slide.What is diagnosis?
a) TT
b) LL
c) Lymphoma
d) Histiocytosis
Answer: TT
Explanation:
Tuberculoid leprosy (TT):
One or few, asymmetrically located lesions
Well defined, hypo-pigmented, anesthetic macules or plaques, often with active border.
The lesions show hair loss and impairment of sweating
A superficial feeder nerve or single regional nerve is often thickened and may even be nodular.
Histopathology:
Hard tubercles eroding into epidermis; no clear zone
Lepromatous leprosy (LL):
A systemic disease characterized by extensive cutaneous, neural and systemic involvement
Histopathology:
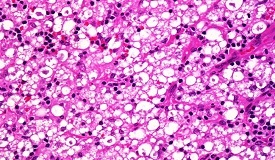
Collection of foamy macrophages in dermis separated from epidermis by a clear zone
Masses of acid-fast bacilli (globi) can be seen in some of the foamy histiocytes
Q-8. A 20 yr old pt with neuro-cysticercosis develops generalised peeling of skin (except palms and soles) starting one month after taking medications for seizures. What is probable diagnosis?
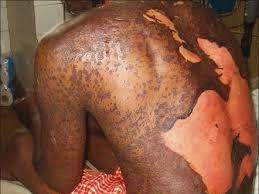
a) SJS
b) TEN
c) Fixed drug eruption
d) Pemphigus vulgaris
Answer: TEN
Explanation:
Drug implicate in Stevens Johnson syndrome and Toxic epidermal necrolysis:
Antibiotics: Sulfonamides, Quinolones, Cephalosporins
Anticonvulsants: Barbiturates, phenytoin, Carbamazepine and Lamotrigine
Anti-tubercular drugs
NSAIDS: Salicylates, ibuprofen, Oxicam group
Miscellaneous drugs: Allopurinol and nevirapine
Important points:
Stevens Johnson syndrome- Body surface area involvement <10 %
Toxic epidermal necrolysis- Body surface area involvement > 30 %
Q-9. A kit of drugs as in following image is implicated for
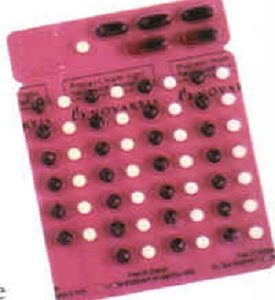
a) Leprosy
b) Urethral discharge
c) Vaginal discharge
d) HIV and AIDS
Answer: Leprosy
Explanation:
MB adult blister pack
MB adult treatment:
Once a month:
Two capsules of rifampicin 300 mg each
Three capsules of clofazimine 100 mg each
One tablet of dapsone 100 mg
Once a day:
One tablet of dapsone 100 mg
One capsule of clofazimine 50 mg
Full course: 12 months with 12 blister packs
Q-10. A smear of was prepared from the genital ulcer. Identify the organism responsible for genital ulcer as shown in below slide
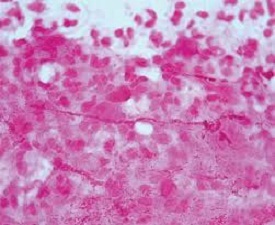
a) H. Ducreyi
b) Chlamydia
c) Gonococcus
d) Treponema pallidum
Answer: H. Ducreyi
Explanation:
H. Ducreyi:
Gram-negative coccobacillus
Cultured on chocolate agar
The characteristic “schools of fish” morphology on staining