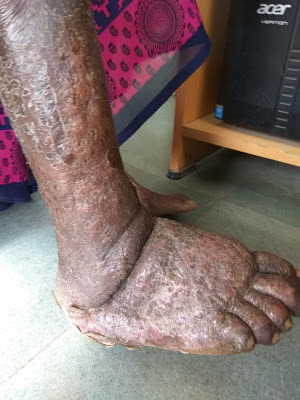
Elephantiasis LegWhat is the cause of Elephantiasis?Lymphatic filariasis, also known as elephantiasis, is caused by parasitic worms of the roundworm family. Elephantiasis results when the parasites lodge in the lymphatic system and lead to chronic obstruction and lymphedema.
What are the round worms which can cause Elephantiasis?Three kinds of round worms cause elephantiasis filariasis: Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori. Of these three, W. bancrofti makes up about 90% of the cases. Man is the only known host of W. bancrofti.
What are the vectors for these filarial worms?Culex, Aedes, and Anopheles mosquitoes are the carriers of W. bancrofti. Anopheles and Mansonia mosquitoes are the carriers of B. malayi. In addition, Anopheles mosquitoes are the carriers of B. timori.
How is Lymphatic filariasis diagnosed?
An active infection is diagnosed by finding the microfilariae via microscopic examination.This may be difficult, as microfilariae only circulate in the blood at night. For this reason, the blood has to be collected nocturnally.The blood should be in the form of a thick smear and stained with Giemsa. Testing the blood for antibodies against the disease may also be used
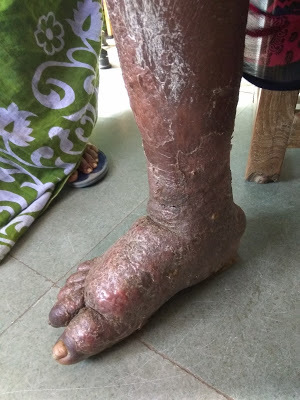
Elephantiasis LegWhat are the various options for conservative management of Filariasis of leg?
Elevation of the limb, exercise, weight reduction. Static isometric activities like prolonged standing or carrying weights should be avoided; rhythmic isotonic movements like swimming/massaging should be encouraged. Benzopyrones are protienolytic agents/lympedim. They are coumarin (I, 2 benzopyrones) derivatives with no anticoagulant effect but increase the lymphatic peristalsis and pumping mechanism along with proteolysis. Daily wearing of below knee stockings. Avoid trauma and infection. Intermittent pneumatic compression devices (Pressure > 50 mmHg); multilayered lymphoedema bandaging (MLLB)— nonelastic type is preferred method; graded stockings. Antibiotics—flucloxacillin, erythromycin, long acting penicillins. Topical antifungal 1% clotrimazole and systemic griseofulvin 250-1000 mg. Regular washing and keeping the limb clean Diethyl carbamazine citrate (DEC) 100 mg TID for 3 weeks. Pain reliefSkin care What are the surgical management options for chronic filarial lymphedema?
a. Excisional
Charle’s operation. Homan’s operation.
b. Physiological
Here either communication between superfi cial and deep lymphatics are created or new lymphatic channels are mobilised to the site.
Omentoplasty. Nodovenous shunt (Neibulowitz). Lymphovenous shunt (O’Brien’s). Ileal mucosal patch.
c. Combined:
Both excision + creation of communication between superfi cial and deep lymphatics.
Sistrunk operation.Thompson’s operation. Kondolean’s operation. Macey’s OperationMiller’s OperationCharle’s Operation
What is Charle’s excisional surgery? Here after excising lymphoedematous tissue, area is covered with skin graft.
What is Homan’s operation? Excision of lymphoedematous tissue is done after raising skin flaps. Later skin flaps are trimmed to required size and sutured primarily. Medial and lateral sides of the limb are done at separate sittings with 6 months interval.
What is Omentoplasty (Omental pedicle)?As omentum contains plenty of lymphatics, omental transfer with pedicle will facilitate lymph drainage.
What is Nodovenous shunt surgery?Nodovenous shunt between iguinal lymph node and long saphenous vein.
What is lymphovenous shunts surgery? Lymphovenous shunts is between dilated lymphatics and long saphenous vein. At least 4 lymphatics should be anastomosed
What is Ileal Mucosal Patch (Kinmonth’s) Surgery?Segment of ileum with pedicle is isolated and opened to expose the mucosa; mucosa is denuded and this mucosa is placed in the thigh as burial to communicate with lymphatics to drain into abdominal lymphatics across ileum.
What is Sistrunk operation?Along with excision of lymphoedematous tissue, window cuts in deep fascia is done, so as to allow communication into normal deep lymphatics.
What is Thompson’s Swiss Roll operation? Lymphoedematous tissue is excised under the skin flaps. Epidermis and part of the dermis of one of the skin flaps is shaved off using Humby’s knife. It is buried under opposite flap, deep to the deep fascia like a swiss roll (Swiss roll operation or buried dermal flap operation).
What is Kondolean’s operation? Along with excision of lymphoedematous tissue, vertical strips of deep fascia is removed so as to open the deep lymphatics which creates communication between superfi cial and deep lymphatics.
What is Macey’s operation? Here skin and subcutaneous tissue are peeled back with deep fascia and split skin grafting is done over the denuded area. Overlying pad of tissue is sutured back temporarily and after 10 days, it is trimmed away
What is Miller’s procedure? It is excision of subcutaneous tissues under the skin flap with deep fascia in two stages. First stage is done over the medial aspect of the limb; second stage done after two months over lateral aspect of the limb.