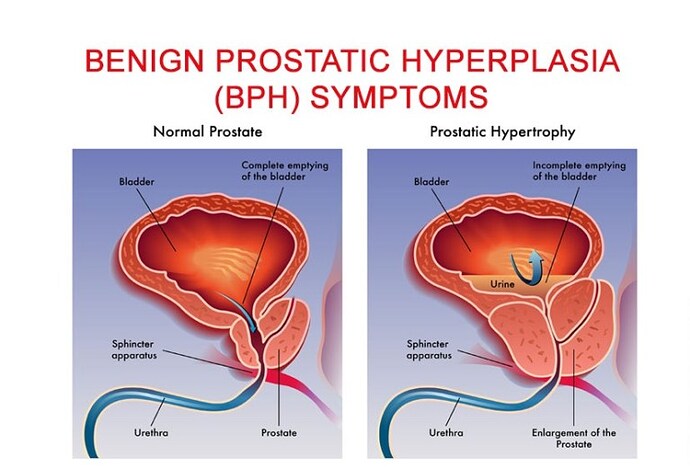
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized organ that surrounds the urethra in men. It is this gland that can become enlarged as men get older, causing a non-cancerous condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia. An enlarged prostate gland can cause a number of annoying symptoms that may cause men to seek medical treatment.
What is BPH?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, often called BPH, is an overgrowth of tissues of the prostate gland. Because of the position of the prostate, this overgrowth can interfere with normal urination. BPH often occurs in men over the age of 40. Though the causes of benign prostates hyperplasia are not known, experts think that testosterone or the chemical it breaks down into, Dihydrotestosterone, may be responsible for the increased growth of prostate tissue. Your physician will check the size of the prostate using a gloved finger inserted into the rectum.
A urinary flow test can help determine the flow of urine through the urethra. A transrectal ultrasound may be used to create an image of the prostate. Intravenous pyelography uses a dye to allow the flow of urine to be seen on x-ray. These tests are used to determine the growth of the prostate gland.
BPH Symptoms
Common enlarged prostate symptoms include the urge to urinate frequently, stopping and starting while urinating, problems starting urination, dribbling after urination and getting up during the night to urinate. Other symptoms may also occur, such as blood in the urine or frequent urinary tract infections. These symptoms can become severe, causing sleep interruption and social embarrassment. In severe cases, urinary retention or incontinence can occur.
BPH Treatment
Treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia includes lifestyles changes and medications that can improve symptoms. Alpha blocker medications, which are usually used to reduce blood pressure, relax the muscles surrounding the bladder, which makes it easier to urinate. Pharmaceutical companies have also developed specific medications that can help reduce the symptoms of BPH. These medications, called 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, reduce the amount of testosterone the converts into Dihydrotestosterone, which causes the prostate to grow. Sometimes, these drugs are used in combination to provide effective treatment of symptoms.
Surgery for BPH
A number of surgical techniques are used to treat BHP. These procedures may include transurethral resection of the prostate, transurethral incision of the prostate, laser surgery to remove prostate tissue or open prostatectomy.